What is the Endocannabinoid System?
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
We like things simple and straightforward at Green Remedy. So, when we dive into explaining the Endocannabinoid System, we aim for the same direct, easy-to-understand approach. With that in mind, let’s answer the question: What is the Endocannabinoid System?
As with anything else, the logical place to start is at the beginning. That said, we must first understand homeostasis before getting into the Endocannabinoid System. Homeostasis is the process an organism (in this case your body) deploys to balance vital systems so that the body can survive in the environment.
What is Homeostasis?
Let’s put homeostasis in terms of coffee temperature; you don’t want it to burn your tongue, nor do you want it too cold. No. You want your coffee just right, the way you like it. Your body is the same way. In order to function properly, your body needs vital systems in balance. The state at which a body regulates itself to maintain ideal conditions is homeostasis. Some processes regulated by homeostasis:
- Blood sugar
- Body temperature
- Blood PH
- Body fluids
- Defense mechanisms:
- Vomiting to expel toxic materials
- Pain response (to heat for example)
- Eyeblink reflex
How is Homeostasis Achieved with the ECS?
This is where the Endocannabinoid System comes in. All humans and vertebrate animals have an Endocannabinoid System (ECS). There are three main components of the ECS system.
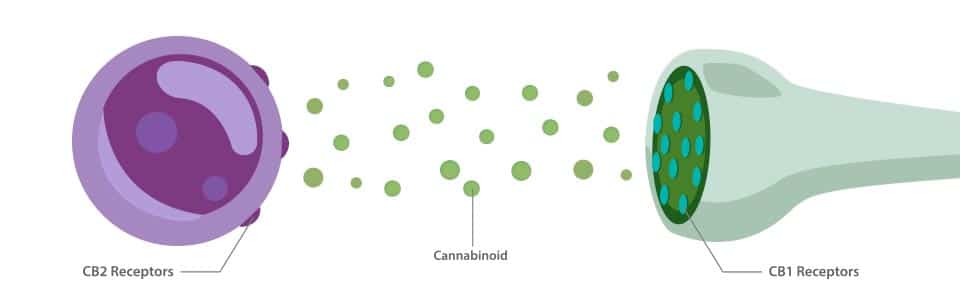
1. Cannabinoid Receptors:
Cannabinoid receptors exist on the surface of cells, “reading” information about conditions surrounding the cell. They send this information to the inside of the cell, which then responds accordingly to the information. They’re kind of like a first alert system.
There are many cannabinoid receptors in the body. Science has knows the most about two, in particular, CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are located in the brain and nervous system, lungs, liver, and kidneys. CB2 receptors are more prominent in the immune system and a few neurons. It’s important to note that these are the prominent locations of both CB1 and CB2 in the endocannabinoid system, but they can be found throughout the body as well.
2. Endocannabinoids:
Endocannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors, activating them. Endocannabinoids are created naturally by cells within the body. In fact, endo literally means internal and/or within. Endocannabinoids such as anandamide and 2-AG are made and utilized when they’re needed. They are not stored.
3. Metabolic Enzymes:
Once they’ve been utilized, metabolic enzymes destroy endocannabinoids. There are two prominent enzymes, FAAH and MAGL. FAAH breaks down anandamide and MAGL destroys 2-AG. The enzymes regulate endocannabinoid use when needed, and how long they’re used. Endocannabinoids are unique this way. They are used as needed, for the duration necessary, then they’re disposed of. Other systems in the body, hormones, for example, can go on for longer periods of time and can even be stored for later use.
CBD Products and The Endocannabinoid System
In conclusion, the Endocannabinoid System serves to achieve homeostasis. When something is out of balance, the ECS system activates to bring it back, when needed, and only for as long as necessary to achieve the goal. When it comes to CBD products and the ECS system, the two work well together. As we take vitamins to help support our body, we look to Green Remedy CBD products to supplement our endocannabinoid system giving it a boost.
References
https://www.projectcbd.org/science/endocannabinoid-system-0
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/homeostasis



